- Age, genetics, joint injuries, and obesity can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
- Common symptoms include pain, stiffness, inflammation, and difficulty in movements.
- Treatment options include medications, physical therapy, weight management, and surgery.
- Knee replacement alternative solutions such as physical therapy, braces, and injections can be used to manage symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes also help reduce the risk of developing osteoarthritis, such as maintaining a healthy weight and exercising regularly.
Osteoarthritis, commonly known as wear-and-tear arthritis, is a degenerative joint disease affecting the cartilage between the bones. It can cause extreme pain, stiffness, and difficulty in movements. It is a common problem affecting millions worldwide, especially the elderly. This blog will thoroughly understand osteoarthritis’s causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a degenerative joint disease that commonly occurs in the hands, hips, knees, and spine and results from the gradual wear and tear on the cartilage that cushions and lubricates joints.
While it can occur at any age, it is more likely to develop in older adults due to the natural aging process. Osteoarthritis causes pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion in affected joints, significantly limiting a person’s ability to carry out daily activities.
Causes of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis often occurs when the protective cartilage cushioning the joints wears down, resulting in pain, stiffness, and inflammation. Osteoarthritis is prevalent in older individuals, and the risk of developing it increases. Here are the primary causes of osteoarthritis and how to manage the condition.
Age
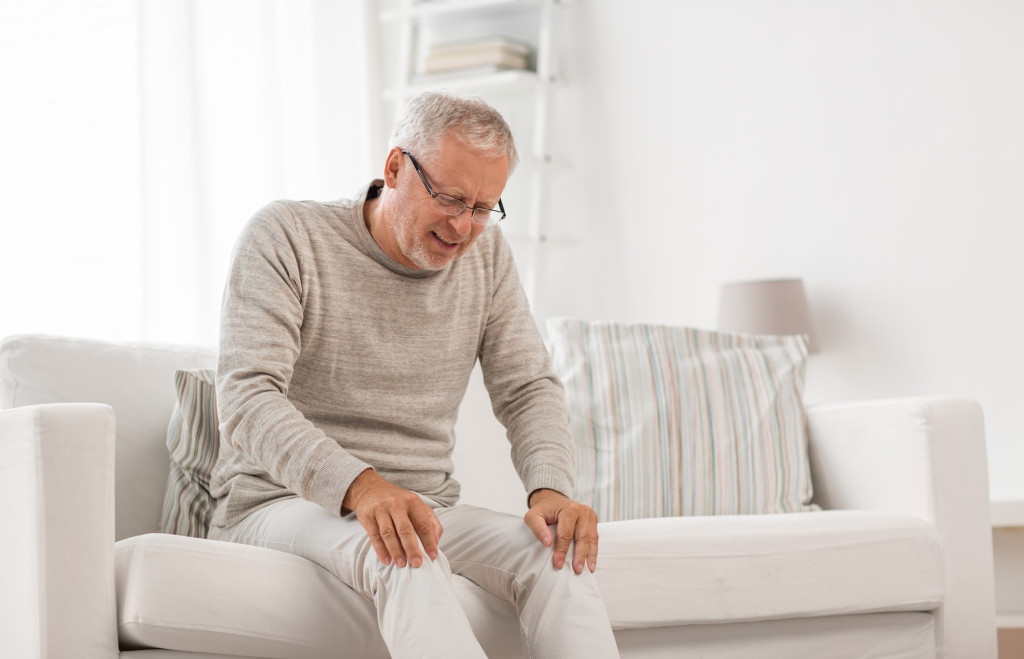

The primary cause of osteoarthritis is age. As the body ages, the protective cartilage around joints tends to degenerate, resulting in chronic pain and stiffness. This is particularly true in the joints of the hands, hips, knees, and spine. Therefore, it is paramount to lead a healthy life during your youth and maintain an exercise routine to enhance bone density and delay the onset of osteoarthritis.
Genetics
Genetics plays a crucial role in the development of osteoarthritis. It is believed that some people may inherit joint abnormalities resulting in cartilage loss at an early age. These genetic predispositions are more common in non-Caucasian populations and promote the development of arthritis. If you have a family history of osteoarthritis, take preventive measures, and seek medical advice to manage the condition as early as possible.
Joint Injuries
In some cases, joint injuries may lead to osteoarthritis. Common injuries resulting from sports, accidents, or falls can weaken cartilage, leading to the onset of osteoarthritis in the future. Experts recommend seeking medical attention for joint injuries early to reduce the risk of chronic pain and arthritis in the future.
Obesity
Obesity can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis, especially in weight-bearing joints such as the hips, knees, and spine. Research has shown that overweight individuals have a higher chance of developing osteoarthritis than individuals with a healthy weight. Obesity increases the pressure on the joints, thus causing accelerated cartilage loss. One way to reduce the risk of osteoarthritis is by maintaining a healthy body weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
The symptoms of Osteoarthritis may vary depending on the severity of the condition and the affected joint. The common symptoms include pain, stiffness, inflammation, and difficulty in movements.
Depending on the joint affected, the pain may be felt during and after activity or resting. The stiffness may be severe in the morning or after sitting long. In some cases, the range of motion in joints may be limited, causing difficulty in performing daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or grasping objects.
Treatments for Osteoarthritis
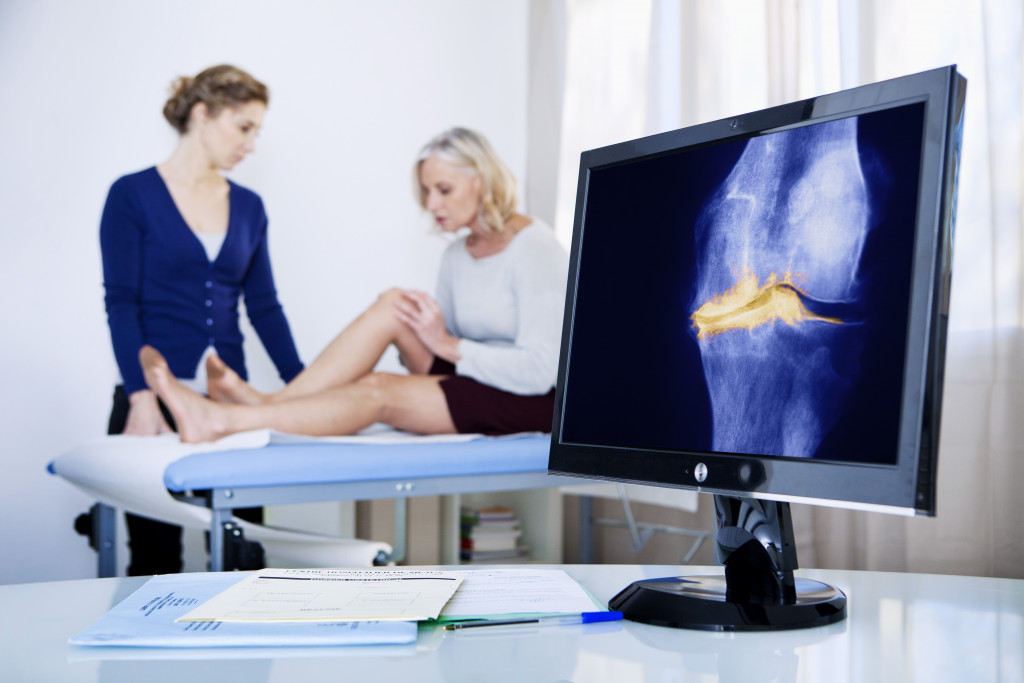
The treatment for Osteoarthritis aims to relieve symptoms, improve joint function, and slow down the progression of the disease. The treatment options include medications, physical therapy, weight management, and surgery.
The treatment may vary depending on where the osteoarthritis is located and how severe it is. For instance, if the pain is primarily felt in the knee, some patients may be recommended to undergo knee replacement surgeries. However, it’s not always the case, as there are knee replacement alternative solutions like physical therapy, braces, and injections to help manage symptoms.
Depending on the severity of your condition, your doctor may suggest treating osteoarthritis with lifestyle changes such as losing weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding activities that put too much stress on joints. In addition to these, medications such as painkillers or anti-inflammatory drugs can also be used to reduce pain and inflammation.
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis is a common joint disorder characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, which can cause pain and stiffness. While no known cure exists for this condition, the symptoms can be managed with proper treatment and lifestyle changes. It’s important to talk to your doctor about what treatment option might work best for you and take steps to reduce the risk of developing osteoarthritis.