- Schizophrenia is a severe mental disorder affecting 1% of the population, characterized by delusions, hallucinations, and more.
- Possible causes may include a combination of genetic, environmental, and brain-chemical imbalances.
- Diagnosis involves medical history evaluation, neurological and laboratory tests, and brain scans.
- Treatment includes psychotherapy, antipsychotic medications, and lifestyle changes.
- Many myths surround schizophrenia, such as it is a split personality disorder or leading to violent behavior; these are not true.
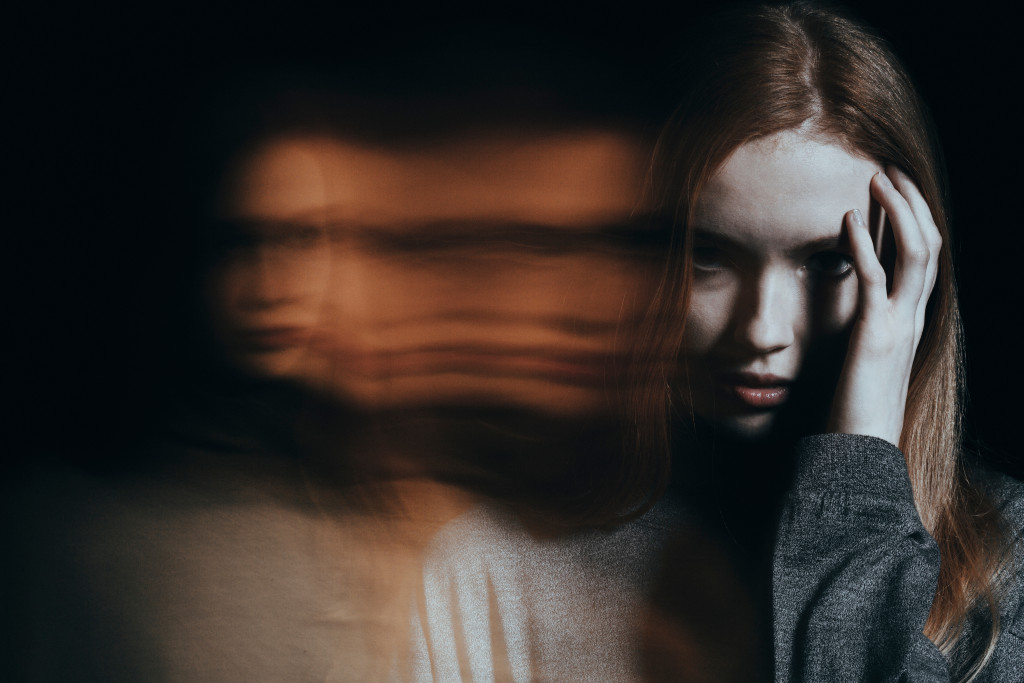
Schizophrenia is a severe and chronic mental disorder that affects nearly one percent of the population globally. It is a complex condition characterized by various symptoms, including delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thinking, and abnormal behavior.
Although the precise cause of schizophrenia is yet to be established, researchers believe that a combination of genetic, environmental, and brain chemical imbalances contributes to the development of this condition. Here’s an in-depth look at schizophrenia, its possible causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and myths surrounding it.
Symptoms
Schizophrenia symptoms are usually classified into Positive, Negative, and Cognitive. Positive symptoms include delusions, hallucinations, disordered thinking, and abnormal behavior. Negative symptoms, on the other hand, include a lack of motivation, disinterest, inability to express emotions, social withdrawal, and reduced speech output. Cognitive symptoms can have problems with memory, attention, and executive functions like decision-making and problem-solving.
Causes
The exact causes of schizophrenia are still a mystery. However, researchers believe that certain variables can lead to schizophrenia. Here are some of them:
Genetics
Research shows that genetics plays a significant role in the development of schizophrenia. People with a family history of schizophrenia are likelier to develop the disorder. Scientists have identified several genes that may contribute to the development of schizophrenia, although the exact mechanisms are not yet well understood.
Neurological Factors
Schizophrenia is also associated with certain neurological factors. For example, there is evidence that people with schizophrenia have abnormalities in some brain regions, including the prefrontal cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Scientists believe these abnormalities may disrupt everyday communication between different parts of the brain, leading to the symptoms of schizophrenia.
Environmental Factors
In addition to genetic and neurological factors, environmental factors may also play a role in the development of schizophrenia. For example, exposure to certain viruses during pregnancy, such as the flu or rubella, has been associated with an increased risk of schizophrenia. Other factors, such as stress, trauma, and substance abuse, may also contribute to the development of the disorder.
Developmental Factors
Schizophrenia typically develops in the late teenage years or early adulthood, although it can occur at any age. Some researchers believe that developmental factors during adolescence may contribute to the development of schizophrenia. For example, there is evidence that people who experience trauma or stress during adolescence are more likely to develop schizophrenia later in life.
Diagnosis
A healthcare professional will typically diagnose schizophrenia based on the patient’s medical history, clinical symptoms, and a series of tests involving neurological and laboratory examinations. The healthcare professional usually uses the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) to diagnose schizophrenia.
Additionally, brain scans can help with diagnosing the disorder. A robust CT scan can see any abnormalities in the brain that may be linked to schizophrenia. Usually, those with the disorder have a smaller brain in certain areas.
Treatment
Thankfully, schizophrenia can be treated in various ways. Here are some of those ways:

Therapy
Those with schizophrenia can benefit from psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or family therapy. CBT helps the patient identify and modify any harmful behaviors and thoughts that may be causing their symptoms. Family therapy helps to improve communication within the family.
Medication
Antipsychotic medications are usually prescribed for schizophrenia patients to reduce their symptoms. These medications can help with delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thinking, and other disorder signs. However, it is essential to note that these medications do not cure schizophrenia; they help manage the symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can also help those with schizophrenia cope with their condition better. This includes engaging in regular physical activity, getting enough sleep each night, and avoiding recreational drugs and excessive alcohol consumption.
Myths
Despite the advances in research, there are still many myths surrounding schizophrenia. For one, it is often considered a split personality disorder; this is not true. Schizophrenia does not cause people to have multiple personalities; it may cause delusions or hallucinations. Additionally, while some with schizophrenia experience violent behavior, this only occurs in a small minority of patients. In most cases, those with schizophrenia are more likely to be victims of violence than perpetrators of it.
Schizophrenia is a complex mental health condition that can affect anyone at any age. While the exact causes are still unknown, genetics and environmental factors appear to play a role in its development. Fortunately, schizophrenia is treatable with therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes. It’s important to stay informed about the condition to dispel misconceptions.

